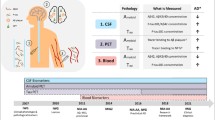
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA) expression varies in association with different tissue types and in diseases. Having been found in body fluids including blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), miRNAs constitute potential biomarkers. CSF miRNAs have been proposed as biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases; however, there is a lack of consensus about the best candidate miRNA biomarkers and there has been variability in results from different research centers, perhaps due to technical factors. Here, we sought to optimize technical parameters for CSF miRNA studies. We examined different RNA isolation methods and performed miRNA expression profiling with TaqMan® miRNA Arrays. More specifically, we developed a customized CSF-miRNA low-density array (TLDA) panel that contains 47 targets: miRNAs shown previously to be relevant to neurodegenerative disease, miRNAs that are abundant in CSF, data normalizers, and controls for potential blood and tissue contamination. The advantages of using this CSF-miRNA TLDA panel include specificity, sensitivity, fast processing and data analysis, and cost effectiveness. We optimized technical parameters for this assay. Further, the TLDA panel can be tailored to other specific purposes. We tested whether the profile of miRNAs in the CSF resembled miRNAs isolated from brain tissue (hippocampus or cerebellum), blood, or the choroid plexus. We found that the CSF miRNA expression profile most closely resembles that of choroid plexus tissue, underscoring the potential importance of choroid plexus-derived signaling through CSF miRNAs. In summary, the TLDA miRNA array panel will enable evaluation and discovery of CSF miRNA biomarkers and can potentially be utilized in clinical diagnosis and disease stage monitoring.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lukiw WJ (2007) Micro-RNA speciation in fetal, adult and Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. Neuroreport 18:297–300. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e3280148e8b
Hebert SS, Horre K, Nicolai L, Papadopoulou AS, Mandemakers W, Silahtaroglu AN, Kauppinen S, Delacourte A et al (2008) Loss of microRNA cluster miR-29a/b-1 in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease correlates with increased BACE1/beta-secretase expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6415–6420. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710263105
Wang WX, Rajeev BW, Stromberg AJ, Ren N, Tang G, Huang Q, Rigoutsos I, Nelson PT (2008) The expression of microRNA miR-107 decreases early in Alzheimer’s disease and may accelerate disease progression through regulation of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci 28:1213–1223. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5065-07.2008
Nelson PT, Wang WX, Rajeev BW (2008) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathol 18:130–138. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00120.x
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH, Lee MJ, Galas DJ, Wang K (2010) The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem 56:1733–1741. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405
Mraz M, Malinova K, Mayer J, Pospisilova S (2009) MicroRNA isolation and stability in stored RNA samples. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:1–4. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.09.061
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D, Wang K (2011) Extracellular microRNA: a new source of biomarkers. Mutat Res 717:85–90. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.03.004
Hebert SS, Nelson PT (2012) Studying microRNAs in the brain: technical lessons learned from the first ten years. Exp Neurol 235:397–401. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.12.004
Nelson PT, Wang WX, Wilfred BR, Tang G (2008) Technical variables in high-throughput miRNA expression profiling: much work remains to be done. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779:758–765. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.03.012
Moldovan L, Batte KE, Trgovcich J, Wisler J, Marsh CB, Piper M (2014) Methodological challenges in utilizing miRNAs as circulating biomarkers. J Cell Mol Med 18:371–390. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12236
Duttagupta R, Jiang R, Gollub J, Getts RC, Jones KW (2011) Impact of cellular miRNAs on circulating miRNA biomarker signatures. PLoS One 6:e20769. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020769
Fourier A, Portelius E, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Quadrio I, Perret-Liaudet A (2015) Pre-analytical and analytical factors influencing Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarker variability. Clin Chim Acta 449:9–15. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2015.05.024
Burgos KL, Javaherian A, Bomprezzi R, Ghaffari L, Rhodes S, Courtright A, Tembe W, Kim S et al (2013) Identification of extracellular miRNA in human cerebrospinal fluid by next-generation sequencing. RNA 19:712–722. doi:10.1261/rna.036863.112
Bekris LM, Lutz F, Montine TJ, Yu CE, Tsuang D, Peskind ER, Leverenz JB (2013) MicroRNA in Alzheimer’s disease: an exploratory study in brain, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. Biomarkers 18:455–466. doi:10.3109/1354750X.2013.814073
Baraniskin A, Kuhnhenn J, Schlegel U, Chan A, Deckert M, Gold R, Maghnouj A, Zollner H et al (2011) Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as marker for primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. Blood 117:3140–3146. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-09-308684
Muller M, Kuiperij HB, Claassen JA, Kusters B, Verbeek MM (2014) MicroRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease: differential expression in hippocampus and cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Neurobiol Aging 35:152–158. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.07.005
Haghikia A, Haghikia A, Hellwig K, Baraniskin A, Holzmann A, Decard BF, Thum T, Gold R (2012) Regulated microRNAs in the CSF of patients with multiple sclerosis: a case-control study. Neurology 79:2166–2170. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182759621
Cogswell JP, Ward J, Taylor IA, Waters M, Shi Y, Cannon B, Kelnar K, Kemppainen J et al (2008) Identification of miRNA changes in Alzheimer’s disease brain and CSF yields putative biomarkers and insights into disease pathways. J Alzheimers Dis 14:27–41
Denk J, Boelmans K, Siegismund C, Lassner D, Arlt S, Jahn H (2015) MicroRNA profiling of CSF reveals potential biomarkers to detect Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 10:e0126423. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126423
Nelson PT, Jicha GA, Schmitt FA, Liu H, Davis DG, Mendiondo MS, Abner EL, Markesbery WR (2007) Clinicopathologic correlations in a large Alzheimer disease center autopsy cohort: neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles “do count” when staging disease severity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:1136–1146. doi:10.1097/nen.0b013e31815c5efb
Schmitt FA, Nelson PT, Abner E, Scheff S, Jicha GA, Smith C, Cooper G, Mendiondo M et al (2012) University of Kentucky Sanders-Brown healthy brain aging volunteers: donor characteristics, procedures and neuropathology. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:724–733
Wang WX, Wilfred BR, Baldwin DA, Isett RB, Ren N, Stromberg A, Nelson PT (2008) Focus on RNA isolation: obtaining RNA for microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling analyses of neural tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779:749–757. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.01.005
Wang WX, Wilfred BR, Madathil SK, Tang G, Hu Y, Dimayuga J, Stromberg AJ, Huang Q et al (2010) miR-107 regulates granulin/progranulin with implications for traumatic brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. Am J Pathol 177:334–345. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.091202
Wang WX, Danaher RJ, Miller CS, Berger JR, Nubia VG, Wilfred BS, Neltner JH, Norris CM et al (2014) Expression of miR-15/107 family microRNAs in human tissues and cultured rat brain cells. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 12:19–30. doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2013.10.003
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T et al (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Mestdagh P, Van Vlierberghe P, De Weer A, Muth D, Westermann F, Speleman F, Vandesompele J (2009) A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biol 10:R64. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-6-r64
Zou GY (2007) Toward using confidence intervals to compare correlations. Psychol Methods 12:399–413. doi:10.1037/1082-989X.12.4.399
Mestdagh P, Feys T, Bernard N, Guenther S, Chen C, Speleman F, Vandesompele J (2008) High-throughput stem-loop RT-qPCR miRNA expression profiling using minute amounts of input RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e143. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn725
Nelson PT, Baldwin DA, Scearce LM, Oberholtzer JC, Tobias JW, Mourelatos Z (2004) Microarray-based, high-throughput gene expression profiling of microRNAs. Nat Methods 1:155–161. doi:10.1038/nmeth717
Mestdagh P, Hartmann N, Baeriswyl L, Andreasen D, Bernard N, Chen C, Cheo D, D’Andrade P et al (2014) Evaluation of quantitative miRNA expression platforms in the microRNA quality control (miRQC) study. Nat Methods 11:809–815. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3014
Chugh P, Dittmer DP (2012) Potential pitfalls in microRNA profiling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 3:601–616. doi:10.1002/wrna.1120
Acknowledgements
Sincere thanks to the research subjects, clinicians, and staff at the UK-ADC. Funding was provided through NIH grants P30 AG028383, R01 AG 042419, and R21 NS085830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
(PPTX 59 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
(PPTX 59 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
(PPTX 59 kb)
Supplementary File 1
(XLSX 110 kb)
Supplementary File 2
(XLSX 93 kb)
Supplementary File 3
(XLSX 68 kb)
Supplementary File 4
(XLSX 28 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 11 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WX., Fardo, D.W., Jicha, G.A. et al. A Customized Quantitative PCR MicroRNA Panel Provides a Technically Robust Context for Studying Neurodegenerative Disease Biomarkers and Indicates a High Correlation Between Cerebrospinal Fluid and Choroid Plexus MicroRNA Expression. Mol Neurobiol 54, 8191–8202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0316-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0316-2